Smart DCA Strategy
SDCA adapts DCA by sizing each buy from market sentiment and risk
Overview
SDCA is an improvement on classic DCA, which invests at a fixed interval. Instead of always investing the same amount, SDCA adjusts the amount per execution based on market sentiment.
Execution diagram
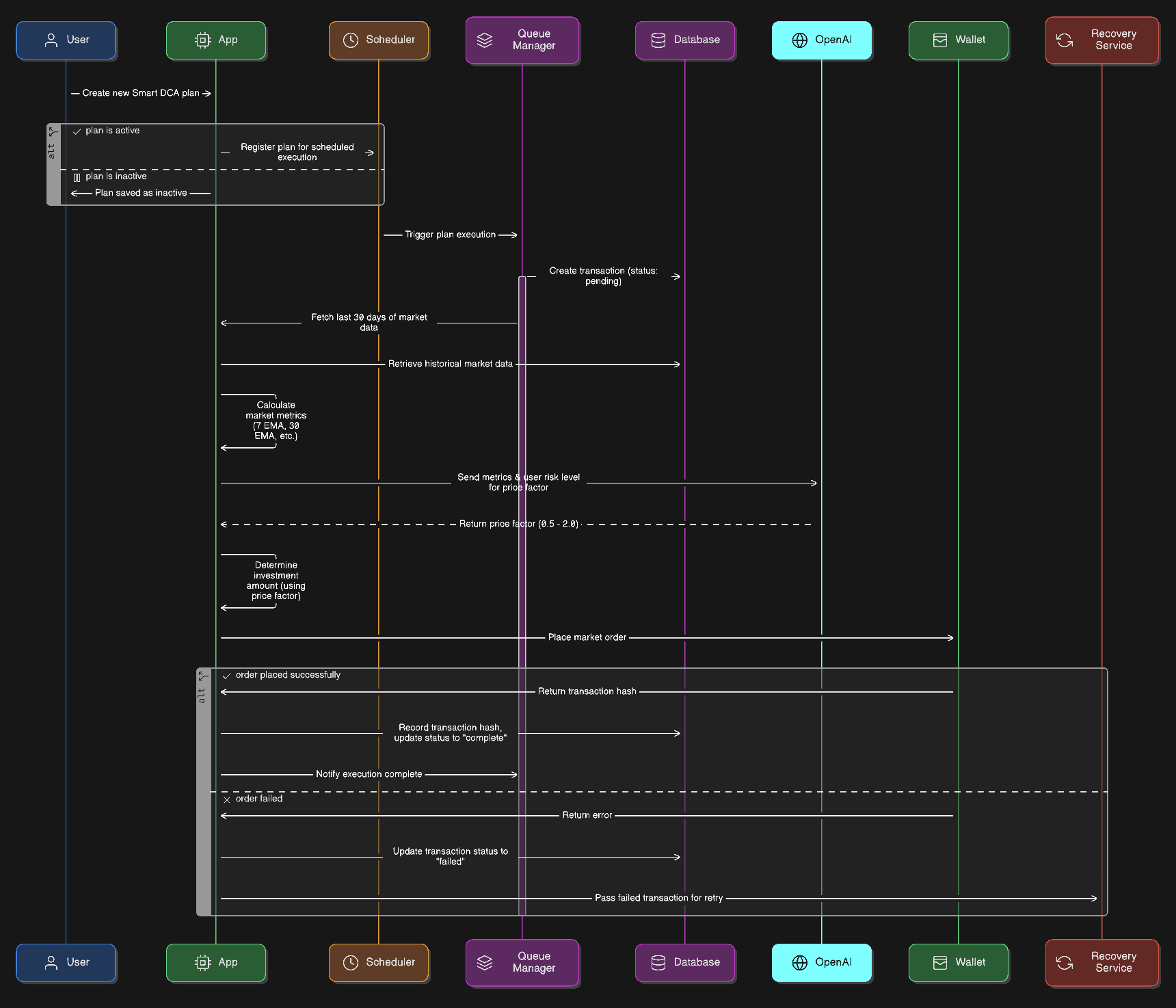
How SDCA differs from DCA
- Fixed schedule, variable size: timing stays periodic, size adapts
- Uses sentiment to scale the buy up or down
- Respects user risk bounds to avoid extreme sizing
Price factor (sentiment multiplier)
We derive a price factor from market sentiment via OpenAI. The price factor is a multiplier in the range [0.5, 2] that determines what fraction of the daily investment to allocate for the current execution.
- Lower expected opportunity → smaller factor
- Higher expected opportunity → larger factor
The factor is computed from metrics such as 30MVA, 7MVA, 30EMA, 7EMA and related trend/volatility signals. A user-selected Risk Level sets the upper and lower bounds that clamp the factor.
Formula:
Optimal Investment = Daily Investment × Price Factor (bounded by risk level)Risk level
- User chooses a risk level that defines min and max bounds for the price factor
- Higher risk allows larger swings in allocation within the [0.5, 2] range
Environments
We run SDCA in two environments:
- Mock: operates on past data (typically a 90‑day window)
- Live: executes in real time using the user’s wallet
Note: mock transactions are not stored in the database to avoid clashes with live state.
Live environment flow
- User creates a plan
- If the plan is active, it is scheduled via cron for its execution time
- At execution time, the job is added to the queue manager
- Queue manager runs the task when a slot is available, in order:
- Create a transaction entry in the database with status pending
- Fetch the last 30 days of data
- Calculate metrics
- Fetch price factor from OpenAI using the computed metrics (sentiment)
- Place a market order to buy the decided quantity
- Update the
txHashand set status complete or failed - Failed transactions are sent to the recovery service for retries
Mock environment: batching and deduplication
Mock runs on historical data. If many users run mock on the same chain and token (with different amounts), we optimize by deduping and batching:
- OpenAI batching computes price factors for 90 days in minimal time
- Dedup links new plans to existing batches when parameters match
- With enough existing plans, most requests reuse prior results and incur no OpenAI overhead
Without batching and dedup, a single 90‑day plan would require about 90 sequential OpenAI calls under a minute, which is rate‑limit prone and costly.
Parameters used for dedup
- Token symbol
- Risk level
- Chain
Amount is not used, since the same factor can be multiplied by different daily investments. With coverage across those three parameters, the hit rate approaches 100 percent.
Mock workflow
- User creates a plan
- Check if an OpenAI batch with the same parameters exists
- If it exists, link this plan to that batch
- Otherwise, create a new OpenAI batch
- Fetch 120 days of data (extra 30 days to seed the first point)
- Calculate metrics for each day across 90 days
- Send a
.jsonlbatch to the OpenAI batch processor - Return batch status (pending or data)
- Query the batch for updates whenever a request is made